FAQs
This FAQ covers NPN & PNP signals and what it means for sensors and Brainboxes Input/Output (IO) modules.
NPN or PNP typically relates to digital signals, with sensor outputs being a common example of devices that can be either NPN or PNP. To connect a sensor, you will need to be able to match the type of signal the device uses.
What is NPN?
NPN stands for Negative, Positive, Negative – also known as Sinking. On an IO module, an NPN input when driven is pulled down to be in a Low state, GND (or a reference voltage level, e.g. V-).
In an NPN transistor, current flows from the emitter to the collector. The transmitter is powered on when sufficient current is supplied to the base of the transistor. The higher the current the more an NPN transistor will be powered on.
A NPN Sensor
NPN Proximity Sensor Output is normally HIGH when nothing is near it.
NPN Proximity Sensor Output goes LOW when metal object is near it.

What is PNP?
PNP stands for Positive, Negative, Positive – also known as Sourcing. On an IO module, a PNP input when driven is pulled up to a High state, e.g. +5V.
A PNP transistor is the opposite to NPN, current flows from the collector to the emitter. The transmitter is powered on when there is no current at the base of the transistor.
For more information on connecting a digital input, please see this FAQ page.
A PNP Sensor
PNP Proximity Sensor Output is normally LOW when nothing is near it.
PNP Proximity Sensor Output goes HIGH when metal object is near it.

What are the Brainboxes ED & BB Logic Levels?
The logic levels for the digital inputs on our ED & BB products are as defined below:
- Logic Level 0 = 0V to +1VDC
- Logic Level 1 = +2V to +30VDC
- Undefined = Between +1V & +2VDC
Please note, that if a voltage is supplied within the undefined range, the input will inconsistently report either 1 or 0.
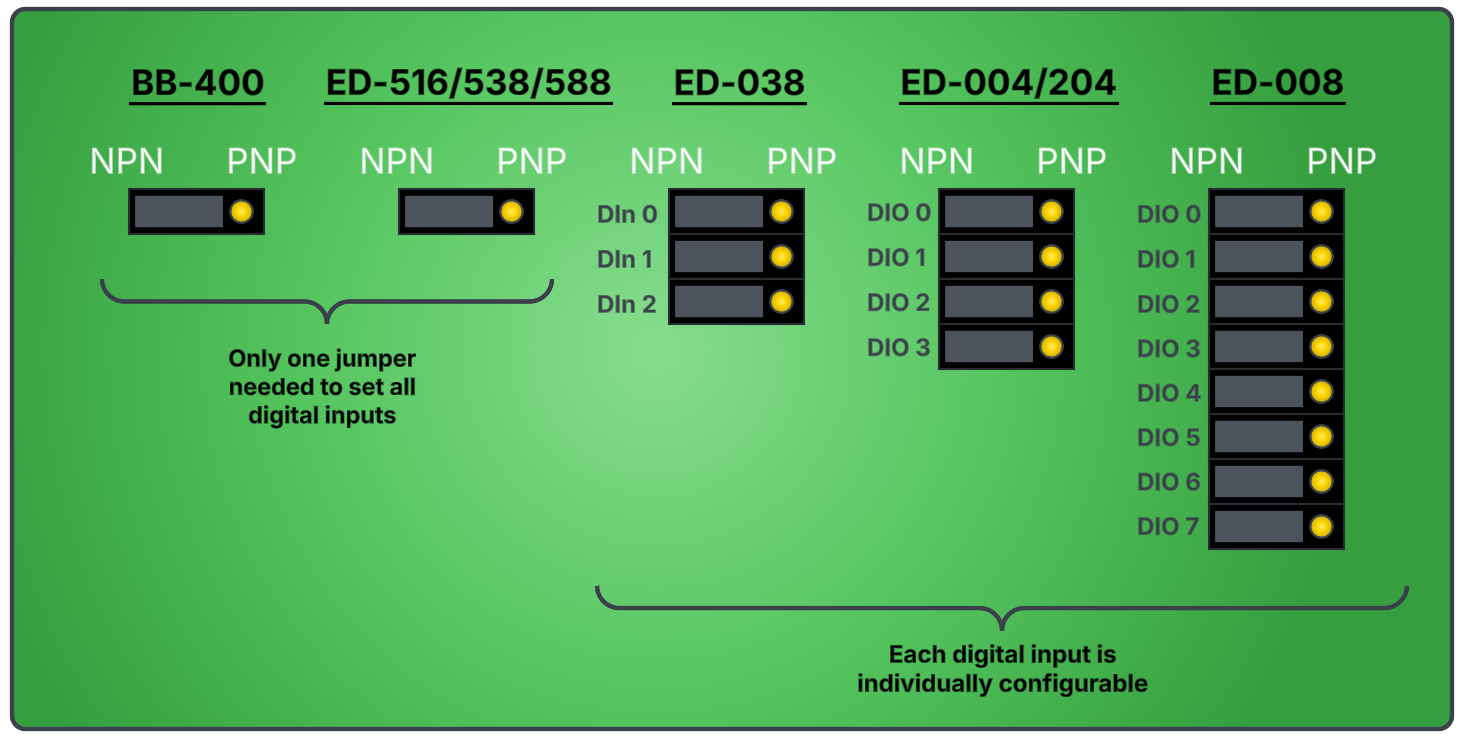
How to locate and set the NPN/PNP jumpers on your Brainboxes Digital Input device
 |
 |
What is the default NPN/PNP configuration for Brainboxes Digital Input devices?
What Digital Outputs are used on Brainboxes ED devices?
Current Sinking (NPN)
Brainboxes IO devices all use Current Sinking outputs (commonly known as NPN outputs). This means that when the output is switched on, it will short the output pin to Ground (GND). Each output can sink a maximum of 30V 0.85A*.
| Max Current Sink (Across All Outputs) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Number of Digital Outputs | Maximum Current Sink per Output (Amps) | |||
| Current (Amps) | Temperature Rating (°C) | Maximum Current Sink Per Output (In Specified Temperature Range) |
|||
| ED-004 & ED-204 | 4 | 0.85A | 3.4A | 0°C to +60°C | 0.85A |
| ED-008 | 8 | 0.85A | 3.4A | 0°C to +60°C | 0.85A |
| ED-527 | 16 | 0.85A | 13.6A | -40°C to +60°C | 0.85A |
| 8A | +60°C to +80°C | 0.5A | |||
| ED-588 | 8 | 0.85A | 6.8A | -40°C to +70°C | 0.85A |
| 4A | +70°C to +80°C | 0.5A | |||
| BB-400 | 8 | 0.85A | 4A | -40°C to +80°C | 0.5A |
Current Sourcing (PNP)
Another type of Digital Output you may encounter is Current Sourcing outputs (also known as PNP outputs). This means that when the output is switched on, it will provide a voltage to whatever is connected to the output pin.
This type of output is not currently natively supported by Brainboxes IO devices, but you can achieve similar functionality with our hardware and some additional circuitry. If you have any questions, or require any further information regarding this please contact: [email protected]